The Importance of Furans Measurement
The Importance of Furans Measurement and Evaluation of Degree of Polymerisation in Transformer Diagnostics
By Andrew Jenkins, Senior Technical Advisor at VPS Power
A transformer’s insulation system consists of oil and paper (including pressboard). As the system ages, the insulating system’s dielectric properties deteriorate. Whilst the ageing of insulating oil can be reversed through oil processing or replacement, if more economical, the ageing of the paper is irreversible. In fact, it can be considered that the life of a transformer is determined by the life of its insulation system.
The paper is composed of cellulose; a polymer consisting of glucose molecules arranged in a long chain. When the paper is exposed to heat, moisture, acid and oxygen, the bonds holding the glucose molecules together begin to break and the paper slowly loses its tensile strength. Severely aged paper can potentially become brittle. Paper degradation is quantified using the term ‘Degree of Polymerisation’ (DP).
In a new transformer, the DP of paper is approximately 1000. At a DP of 450-500, the paper is deemed to have lost approximately 50% of its tensile strength. A DP of 200 is considered in the industry as the absolute end-of-life value acceptable for a transformer in service.
However, a transformer with such a low DP can continue to operate normally providing it does not experience any external events. In a situation where the load is suddenly changed, the transformer is subjected to mechanical shock, or there is a through fault on the system, the transformer has a higher risk of failing.
Glucose is an unstable molecule, so it can quickly convert into chemicals known as furans. A furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring structure containing four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom.
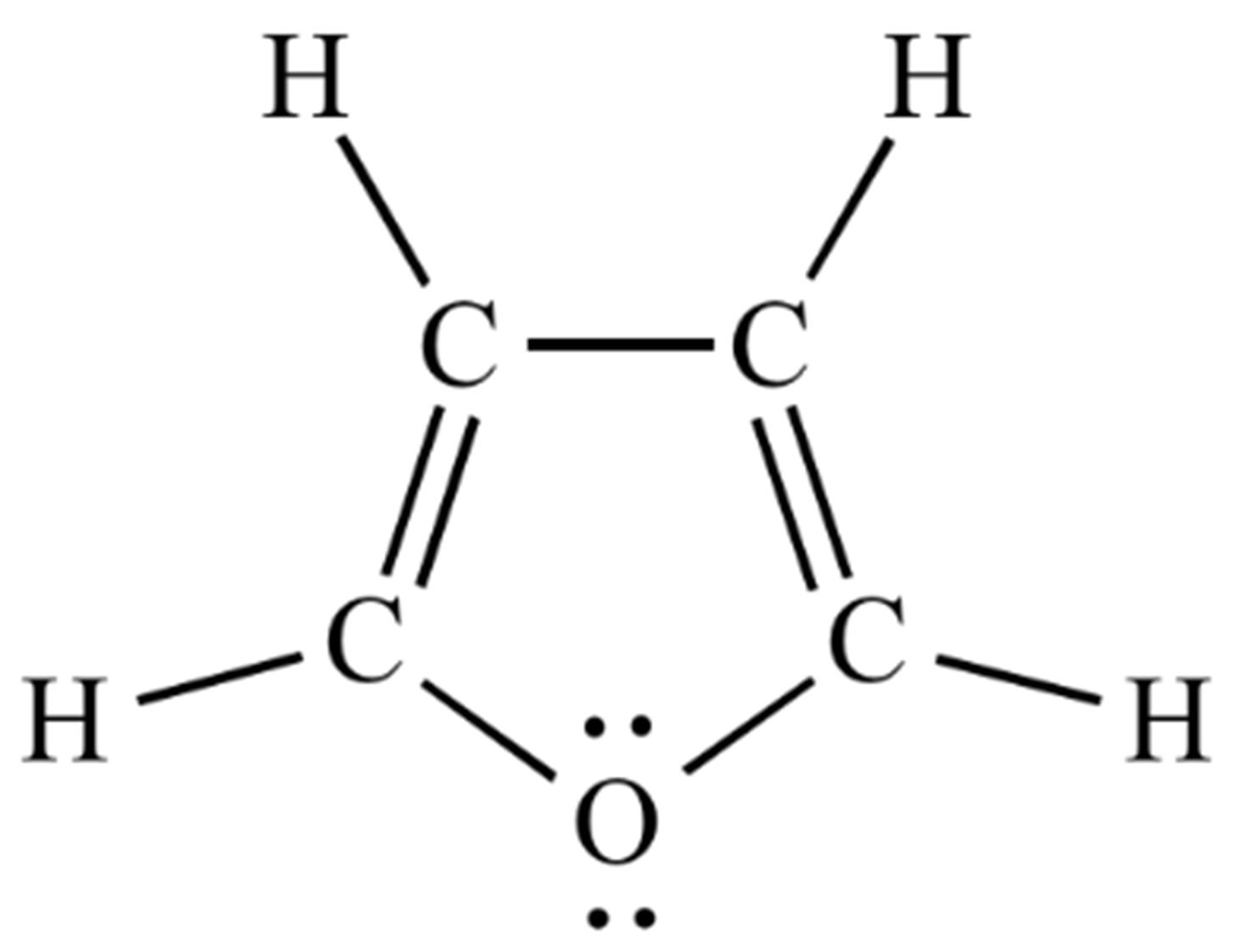
Furans are only produced in transformers through the degradation of cellulose and subsequently are an ideal parameter for determining the condition of the paper insulation.
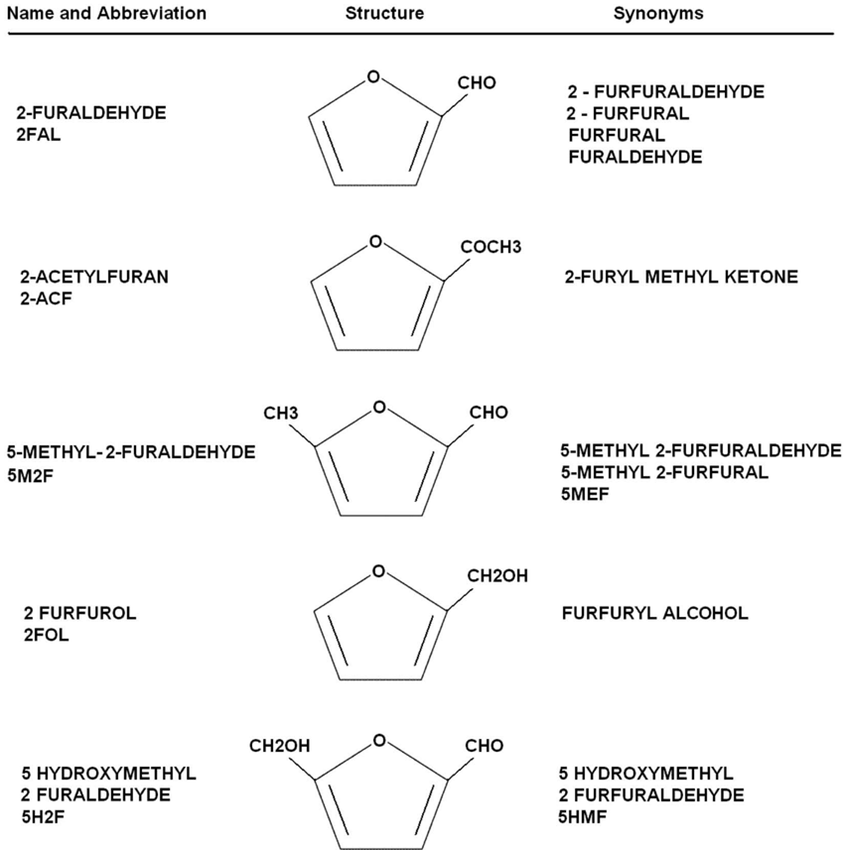
The presence of the following furans can be detected as part of the VPS Power transformer oil conditioning monitoring program:
- 2-furaldehyde or furfural (2FAL) caused by general overheating or normal ageing.
- 5-methyl-2-furaldehyde (5M2F) caused by localised severe overheating (hotspot).
- 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furaldehyde (5H2F) – caused by oxidation.
- 2-acetylfuran (2ACF) – rare, causes not fully defined, although lightning strikes are a possible cause.
- 2-furfurol (2FOL) – caused by high moisture in the paper:
2FAL is the most abundant and most stable of these derivatives and therefore its concentration in oil can be used to estimate the DP of the paper insulation.
Determining the actual DP is intrusive, costly, and possibly damaging to transformers as it requires taking paper samples for analysis. Laboratory studies have shown that there is good correlation between estimated and actual DP, although it is not 100% accurate.
There are many equations for calculating the estimated DP of paper. For example, Pahlavanpour’s model assumes that paper ageing is not uniform and that 20% of the inner paper layers in the windings degrade twice as fast as the rest of the paper and Stebbins proposed an equation for thermally upgraded paper. Deviations from model to model are also due to different ageing factors and ageing assumptions. Chendong was one of the first people to develop an equation for calculating estimated DP, which was based on data collected from transformers that have normal Kraft paper and free breathing conservators. When comparing several models, Chendong’s model gives the lowest DP value for a given furan concentration, so will give the lowest overestimation or possible underestimation for transformers with thermally upgraded paper, which is deemed to be safer. Therefore, it has been concluded that the Chendong model can be used for any transformer, irrespective of the type of insulation paper and whether a transformer is free breathing or not.
The Chendong model is expressed as shown in the following equation:
DP = log(2FAL) - 1.51
-0.0035
Where the concentration of 2FAL is in ppm (mg/kg)
Based on this, VPS recommends the use of the Chendong model for estimating the DP of paper. It should be noted that oil processing or replacement can remove evidence of paper degradation, although the degradation itself is irreversible. However, it’s important to note, estimated DP should not be calculated if remedial action has occurred within the past few years.
For further advice and information regarding Furan monitoring and transformer insulating system degradation, please contact: power@vpsveritas.com
 Search
Search
 Customer
Customer